Cyber threats are no longer a distant risk; they’re a daily reality for businesses of all sizes. From ransomware to scams, attacks are becoming more sophisticated, frequent, and costly. According to the U.S. Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), small businesses now account for 43% of cyberattacks, with incidents rising dramatically since the pandemic.
This raises a critical question for organizations worldwide: should you build an in-house cybersecurity team, or should you outsource cybersecurity to specialized providers?
The answer isn’t one-size-fits-all. It depends on your budget, risk profile, compliance requirements, and growth plans. In this article, we’ll break down the pros and cons of outsourced vs in-house cybersecurity, share practical tips, and explore why outsourcing, especially to talent hubs like Malaysia, may be a game-changer for global employers.
Content Outline
Key Summary
Cybersecurity is Critical for Business Continuity
Protecting your digital assets is more than technical, it safeguards customer trust, ensures compliance with laws like GDPR and Singapore’s Cybersecurity Act, and prevents costly disruptions.
Outsourced Cybersecurity Provides Speed and Expertise
Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) offer immediate deployment, 24/7 monitoring, and access to specialized knowledge. Example: A fintech startup can outsource cybersecurity roles to Malaysia through FastLaneRecruit for rapid market expansion.
In-House Teams Offer Control and Deep Organizational Knowledge
Internal cybersecurity teams understand company-specific systems, culture, and processes, allowing for immediate response and integration with physical security.
Hybrid Approach Balances Control and Flexibility
Combining an internal team for daily monitoring with outsourced specialists for complex tasks ensures comprehensive protection, cost efficiency, and compliance support.
Cost, Talent, and Scalability Are Key Considerations
Evaluate total cost of ownership (salaries, training, hardware), talent availability, and growth plans to determine which cybersecurity model best suits your organization.
Malaysia as a Cybersecurity Outsourcing Hub
Malaysia offers highly skilled professionals, cost-effective operations, and regional compliance expertise. Using FastLaneRecruit’s EOR service allows global companies to hire cybersecurity talent without establishing a local entity.
Make Informed Decisions Using Risk and Compliance Assessments
Assess your risk profile using frameworks like NIST, consider regulatory obligations, and match your cybersecurity strategy to your business size, industry, and expansion plans.
FastLaneRecruit Simplifies Cybersecurity Outsourcing
Outsource Malaysian cybersecurity professionals quickly, compliantly, and efficiently to secure your business against evolving threats and scale your team as needed.
Why Cybersecurity Matters More Than Ever
Cybersecurity today goes far beyond installing firewalls or setting strong passwords. It is about safeguarding your business continuity, protecting customer trust, and meeting strict compliance requirements in an increasingly digital-first world.
A single cyber incident can cripple operations, damage reputation, and even lead to costly regulatory penalties. For example:
- A small e-commerce business in Asia that suffers a data breach may lose customers overnight if credit card details are exposed.
- A financial services firm in the EU that fails to meet the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) standards could face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of its annual global turnover, whichever is higher.
- Companies operating in Singapore must comply with the Cybersecurity Act, which empowers regulators to investigate and enforce strict measures if critical information infrastructures are compromised.
Frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework provide guidance on how businesses can identify risks, protect systems, detect threats, respond quickly, and recover effectively. But applying these standards requires resources, expertise, and strategic planning.
The stakes are only getting higher. According to Cybersecurity Ventures, the global cost of cybercrime is expected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. This includes everything from ransomware payments and downtime costs to data recovery and regulatory fines.
Whether you run a startup in Malaysia, a multinational in the U.S., or a trading company in Hong Kong, the decision is the same:
- Should you hire and train your own cybersecurity team?
- Should you outsource to an experienced external provider?
- Or should you adopt a hybrid approach that balances both?
Making this decision early and aligning it with your growth and compliance needs is critical to building a resilient business in the digital age.
Also Read: What You Need To Know About Gen X Work Ethic
What is Outsourced Cybersecurity?
Outsourced cybersecurity is the practice of hiring an external provider, commonly known as a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP), to take over some or all aspects of your company’s cybersecurity operations. Instead of building an entire security team in-house, you rely on specialists who already have the tools, processes, and expertise in place.
The scope of outsourced cybersecurity can be tailored to your business needs. It may include:
- 24/7 Network Monitoring – Continuous surveillance to detect suspicious activity and prevent breaches.
- Incident Response – Rapid containment and recovery in the event of a cyberattack.
- Compliance Audits – Ensuring your systems meet international and local regulatory standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, or the Cybersecurity Act in Singapore).
- Penetration Testing – Simulating attacks to identify and fix vulnerabilities before hackers exploit them.
- Threat Intelligence Services – Accessing real-time insights about global cyber threats.
Think of outsourcing cybersecurity like hiring a dedicated security guard for your digital assets, but one who doesn’t just watch the door. They also install cameras, monitor the building 24/7, and know how to respond if someone tries to break in.
Example in Practice
Imagine a U.S.-based fintech startup that wants to expand into Asia. Setting up an in-house cybersecurity team in each new country would be slow and expensive. Instead, the company could:
- Outsource cybersecurity roles to Malaysia through FastLaneRecruit’s Employer of Record (EOR) service.
- Gain immediate access to highly trained cybersecurity analysts familiar with regional compliance requirements.
- Avoid the cost and complexity of setting up a local entity, handling payroll, or navigating employment laws.
This approach gives the startup scalability and flexibility; they can ramp up their security capabilities as they grow, without the long lead time of recruiting and training an internal team.
In short, outsourced cybersecurity offers a faster, cost-effective, and expertise-driven alternative to securing your business against rising cyber threats.
Outsourced vs In-House Cybersecurity: Key Differences
Choosing between outsourced and in-house cybersecurity comes down to several critical factors. Below, we break each one down to help you make an informed decision.
Also Read: How to Successfully Outsource a Back-End Development Team
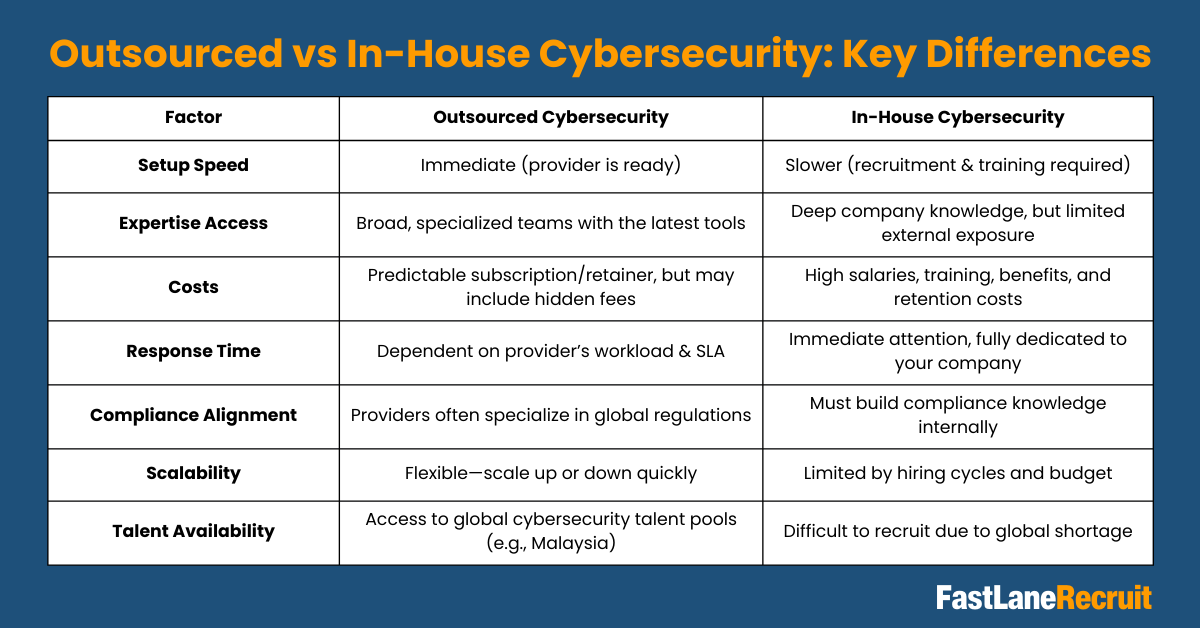
Setup Speed
Outsourced Cybersecurity: One of the biggest advantages of outsourcing is speed. Providers already have infrastructure, tools, and trained personnel ready to deploy. Once a contract is signed, your business can start benefiting from cybersecurity coverage almost immediately.
Example: A global e-commerce company expanding into Malaysia could outsource security monitoring through FastLaneRecruit’s EOR service and have a team in place within weeks, avoiding months of recruitment and setup.
In-House Cybersecurity: Building a team from scratch is slower. Recruiting skilled professionals, setting up monitoring systems, and training employees takes time, often several months. This can leave your organization exposed during the ramp-up period.
Expertise Access
Outsourced Cybersecurity: External providers bring specialized knowledge gained from working with multiple industries and threat scenarios. Their teams are often trained on the latest technologies and frameworks, giving businesses access to cutting-edge tools without hiring multiple experts.
In-House Cybersecurity: Internal teams have deep knowledge of your company’s operations, culture, and systems. However, they may have limited exposure to emerging global threats or advanced tools if the organization doesn’t continuously invest in training and technology.
Costs
Outsourced Cybersecurity: Costs are generally predictable through subscription fees or retainer agreements. While there may be additional fees for special services or hardware, outsourcing often saves money compared to hiring full-time specialists.
In-House Cybersecurity: Employing a full-time team requires paying salaries, benefits, training, and handling retention. For small or medium-sized businesses, these costs can quickly add up and strain budgets.
Example: A startup in Singapore may spend 3–5x less outsourcing a Malaysian cybersecurity analyst via an EOR service than hiring locally with full employment benefits.
Response Time
Outsourced Cybersecurity: Providers promise quick responses, but actual response times can vary based on their workload and service-level agreements (SLAs). During major incidents, your issue might not be the highest priority.
In-House Cybersecurity: Teams are fully dedicated to your organization, providing immediate attention whenever a threat is detected. This direct focus can help contain attacks faster and reduce potential damage.
Compliance Alignment
Outsourced Cybersecurity: Many MSSPs are well-versed in global compliance standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001. They can help ensure that your systems meet legal requirements efficiently.
In-House Cybersecurity: Internal teams must develop compliance knowledge on their own. This can be time-consuming and may require hiring specialists to navigate complex regulations.
Scalability
Outsourced Cybersecurity: External providers offer flexibility to scale services up or down as your business grows or faces varying threat levels. This allows organizations to adapt without long recruitment cycles.
In-House Cybersecurity: Expanding an internal team is limited by hiring timelines, budget constraints, and employee availability. Scaling up can be slower and more expensive.
Also Read: How to Hire and Manage a High-Performing Back-End Developer Team in Malaysia
Talent Availability
Outsourced Cybersecurity: Outsourcing opens access to global talent pools. For example, companies can hire experienced cybersecurity professionals in Malaysia through FastLaneRecruit’s EOR service, gaining expertise at competitive rates.
In-House Cybersecurity: Recruiting skilled cybersecurity professionals locally can be challenging due to a global talent shortage. Retaining experts is also difficult, as high demand often leads to turnover and job-hopping.
Summary Table
| Factor | Outsourced Cybersecurity | In-House Cybersecurity |
| Setup Speed | Immediate (provider is ready) | Slower (recruitment & training required) |
| Expertise Access | Broad, specialized teams with the latest tools | Deep company knowledge, but limited external exposure |
| Costs | Predictable subscription/retainer, but may include hidden fees | High salaries, training, benefits, and retention costs |
| Response Time | Dependent on provider’s workload & SLA | Immediate attention, fully dedicated to your company |
| Compliance Alignment | Providers often specialize in global regulations | Must build compliance knowledge internally |
| Scalability | Flexible—scale up or down quickly | Limited by hiring cycles and budget |
| Talent Availability | Access to global cybersecurity talent pools (e.g., Malaysia) | Difficult to recruit due to global shortage |
Pros and Cons of Outsourcing Cybersecurity
Outsourcing cybersecurity can be a highly effective strategy for businesses looking to strengthen their digital defenses without building a full internal team. However, like any approach, it has both advantages and potential drawbacks.
Benefits
Access to Expertise
Outsourced cybersecurity providers work with a wide range of industries and threat scenarios every day. Their teams include specialists in areas like threat detection, incident response, penetration testing, and cloud security.
Example: A fintech startup expanding operations in Asia can tap into a provider’s expertise in regional phishing schemes or ransomware trends without having to train internal staff. This ensures your company benefits from knowledge that would take years to develop in-house.
24/7 Monitoring
Cyberattacks don’t follow business hours. Outsourced providers typically offer round-the-clock monitoring, helping detect and respond to threats instantly, even outside your normal workday.
Example: A Malaysian e-commerce business that operates globally can rely on outsourced teams to monitor servers overnight, preventing potential downtime during peak shopping hours in the U.S. or Europe.
Cost Efficiency
Hiring and retaining a skilled in-house cybersecurity team is expensive, with salaries, benefits, and ongoing training costs. Outsourcing allows companies to access top-tier talent at a fraction of the cost.
Example: Instead of recruiting three full-time cybersecurity analysts in Singapore, a company can hire a team through FastLaneRecruit’s EOR service in Malaysia, gaining the same level of expertise for significantly lower operational costs.
Also Read: Payroll and Compliance for Hiring Back-End Developers in Malaysia
Faster Deployment
When time is critical, outsourced providers can implement solutions immediately. There’s no need to go through lengthy recruitment, onboarding, or infrastructure setup.
Example: A growing SaaS company launching a new product in multiple regions can have MSSPs deploy monitoring tools and security protocols within days instead of months.
Compliance Support
Keeping up with global regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001 can be challenging. Outsourced providers often specialize in compliance, helping ensure your business meets legal standards efficiently.
Example: A healthcare startup storing patient data in multiple countries can rely on outsourced experts to navigate local data protection laws without hiring dedicated legal or compliance staff.
Drawbacks
Hidden Costs
While outsourcing can be cost-effective, unexpected expenses may arise. Hardware upgrades, additional licenses, or emergency interventions may not be included in the base contract.
Example: If a cybersecurity incident requires deploying new servers or cloud-based tools, your monthly outsourcing fee might increase unexpectedly.
Less Control
When you outsource, you are one of many clients. This can limit your ability to directly influence decisions or customize processes.
Example: An international trading company relying on an MSSP may have to follow standard security protocols rather than fully tailoring every process to its unique systems.
Response Delays
Even with promised SLAs, response times can vary. During widespread cyberattacks, priority may be given to larger clients or those under severe threat, leaving smaller businesses temporarily exposed.
Example: A mid-sized e-commerce company experiencing a phishing attack may need to wait for the provider to allocate resources if other clients are facing critical breaches simultaneously.
Pros and Cons of In-House Cybersecurity
Building an in-house cybersecurity team gives your organization direct control and deep knowledge of internal systems. However, it also comes with challenges that can affect cost, scalability, and talent retention.
Benefits
Direct Control
An internal team works exclusively for your organization, allowing you to set priorities, oversee operations, and make decisions quickly. You control the workflow and can adjust strategies to meet evolving needs without relying on third-party approval.
Example: A large e-commerce company in Singapore can immediately shift its in-house team to address a sudden spike in phishing attempts targeting its payment platform, without waiting for external vendors to respond.
Deeper Organizational Knowledge
In-house cybersecurity professionals develop a comprehensive understanding of your systems, processes, and culture. This enables them to anticipate vulnerabilities and tailor security strategies to your business needs.
Example: A fintech startup with proprietary trading algorithms benefits from an internal team that understands not only the technical infrastructure but also the regulatory and operational nuances of the company.
Integrated Security
Internal teams can coordinate cybersecurity efforts with other aspects of security, including physical access controls, video surveillance, and IT policies, creating a holistic defense strategy.
Example: A logistics company can ensure that both warehouse access systems and networked IoT devices are secured, reducing the risk of breaches that span both physical and digital domains.
Immediate Response
When threats arise, in-house teams can act instantly, without waiting for external approvals or service-level agreements. This quick response can prevent small issues from becoming major incidents.
Example: If malware is detected on a corporate network during off-hours, the internal team can immediately isolate affected devices and contain the threat before data is lost.
Also Read: Why Global Companies Choose Malaysia for Offshore Back-end Development
Drawbacks
High Costs
Maintaining an in-house cybersecurity team requires significant investment in salaries, benefits, training, and technology. These costs can be especially challenging for small and medium-sized businesses.
Example: Hiring three cybersecurity analysts in Hong Kong may cost as much as outsourcing a full team in Malaysia through FastLaneRecruit’s EOR service, including all payroll and compliance overheads.
Talent Shortages
Cybersecurity professionals are in high demand globally, making it difficult to recruit and retain skilled staff. This talent gap can leave critical positions unfilled for months.
Example: A medium-sized SaaS company may struggle to hire analysts trained in cloud security and incident response because qualified candidates are scarce.
Retention Issues
Even after successfully hiring experts, retaining them is challenging. Professionals may leave for higher salaries, consulting opportunities, or international roles, creating disruption and knowledge gaps.
Example: An in-house security specialist who has learned proprietary systems might leave for a consulting role abroad, forcing the company to restart recruitment and onboarding.
Key-Person Risk
Relying heavily on one or two experts can be risky. If a key team member leaves or is unavailable, the organization may face critical knowledge gaps or operational delays.
Example: A trading company’s entire incident response plan might depend on a single cybersecurity engineer. If that person is unavailable during an attack, response could be slow or inadequate, resulting in data loss or financial damage.
Hybrid Approach: The Best of Both Worlds?
For many organizations, the choice between fully in-house or fully outsourced cybersecurity doesn’t have to be binary. A hybrid approach combines the strengths of both models, giving businesses the flexibility to maintain control while accessing specialized expertise.
How a Hybrid Model Works
- In-House Team for Core Operations
An internal team handles day-to-day cybersecurity operations, such as monitoring internal networks, managing access controls, and responding immediately to low- to medium-level threats. This ensures that the organization has direct control over its most sensitive systems and can act quickly without delays.
Example: A logistics company in Singapore maintains a small internal cybersecurity team that monitors warehouse IoT devices and corporate servers in real-time. This team can instantly respond if an anomaly is detected, preventing operational disruption.
- Outsourced Experts for Specialized Tasks
External providers are brought in for complex or high-stakes tasks that require specialized knowledge or advanced tools. This includes activities such as:
- Forensic investigations following a breach
- Penetration testing by advanced ethical hackers
- Compliance audits for regulations like GDPR or ISO 27001
- Threat intelligence analysis for emerging global threats
Example: The same logistics company outsources regulatory audits and penetration testing to a managed security service provider (MSSP) in Malaysia through FastLaneRecruit’s EOR service. This allows the company to access regional expertise and advanced tools without hiring full-time specialists.
Also Read: How to Outsource App Development in 2025
Benefits of a Hybrid Approach
- Balanced Control and Flexibility: The internal team keeps control over daily operations, while the external provider offers scalable expertise.
- Cost Optimization: Instead of building a large in-house team for rare or advanced tasks, companies only pay for specialized services when needed.
- Enhanced Security Coverage: Combining in-house vigilance with outsourced advanced expertise ensures comprehensive protection against both common and sophisticated threats.
- Regulatory Compliance Made Easier: Outsourced specialists can guide complex audits, reducing the risk of non-compliance fines.
Considerations for Success
While a hybrid model can be highly effective, it requires careful coordination between internal staff and external providers. Clear communication, defined responsibilities, and shared protocols are essential to avoid gaps or overlapping efforts.
Example: A fintech startup using a hybrid model sets up weekly coordination meetings between its in-house analysts and outsourced MSSP team. This ensures that security incidents are addressed promptly and that compliance audits are aligned with internal operations.
Tips for Deciding Between Outsourced vs In-House Cybersecurity
Choosing the right cybersecurity model is a critical decision that can affect business continuity, cost efficiency, and regulatory compliance. Consider the following tips to make an informed choice:
1. Assess Your Risk Profile
Start by evaluating your organization’s exposure to cyber threats. Use frameworks like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework to identify vulnerabilities in your systems, processes, and networks.
Example: A mid-sized e-commerce company might find that its online payment gateway and customer database are high-risk areas. This insight can help determine whether specialized outsourced expertise is needed for continuous monitoring or if a small in-house team is sufficient.
2. Calculate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
When comparing in-house vs. outsourced cybersecurity, look beyond basic salaries. Consider training, software and hardware costs, employee turnover, downtime from breaches, and long-term operational expenses.
Example: A healthcare startup in Singapore may discover that hiring three full-time cybersecurity analysts will cost more over three years than outsourcing the same roles to Malaysia via FastLaneRecruit’s EOR service, factoring in benefits, training, and recruitment cycles.
3. Consider Regulatory Obligations
Compliance requirements vary by industry and geography. Finance, healthcare, and e-commerce companies often face stricter cybersecurity regulations, including data privacy laws and mandatory reporting of breaches.
Example: A fintech firm handling cross-border transactions might rely on outsourced cybersecurity experts familiar with GDPR, MAS regulations, and ISO 27001 to ensure that its systems meet all legal requirements efficiently.
4. Think About Growth and Scalability
Rapidly growing businesses need flexibility. Outsourced cybersecurity allows you to scale services up or down as your operations expand, without the delays of recruitment or training.
Example: A SaaS company launching in multiple Southeast Asian markets can use outsourced cybersecurity teams to cover each region immediately, while planning a small in-house team to manage day-to-day monitoring.
5. Leverage Global Talent Pools
Outsourcing opens access to skilled professionals in regions where cybersecurity expertise is abundant and costs are competitive.
Example: Companies can hire experienced Malaysian cybersecurity professionals through FastLaneRecruit’s EOR service, gaining high-level expertise at a fraction of the cost of hiring locally, all without the need to establish a legal entity in Malaysia.
Bonus Tip: Consider a Hybrid Approach
For many businesses, combining in-house and outsourced cybersecurity teams provides the best balance of control, expertise, and cost-efficiency. Maintain an internal team for immediate response while outsourcing specialized tasks like penetration testing, compliance audits, or advanced threat monitoring.
Example: A growing logistics company uses an internal team for daily network monitoring and outsources compliance and forensic investigations to a managed service provider, ensuring both fast response times and access to expert knowledge.
Why Outsource Cybersecurity to Malaysia?
Malaysia has become a strategic hub for cybersecurity talent in Southeast Asia, offering a unique combination of expertise, cost efficiency, and regional knowledge. Here’s why businesses increasingly choose Malaysia for outsourced cybersecurity:
1. Access to Skilled Professionals
Malaysia has a growing pool of highly trained cybersecurity experts with experience in global standards, cloud security, and incident response.
Also Read: Why Malaysia Is the Ideal Country to Hire Offshore App Developer
2. Cost-Effective Operations
Hiring experienced cybersecurity talent in Malaysia is often significantly more affordable than in Western countries or some neighboring Asian markets, without compromising on quality.
3. Strong Regional Expertise
Malaysian cybersecurity professionals are well-versed in both regional compliance standards and international regulations, making them ideal for businesses operating across Southeast Asia.
4. Flexible and Scalable Teams
Outsourcing to Malaysia allows businesses to scale cybersecurity teams up or down quickly, depending on business growth or emerging threats.
5. Faster Market Entry Without Legal Barriers
Through services like FastLaneRecruit’s Employer of Record (EOR) solution, companies can hire cybersecurity talent in Malaysia without establishing a local legal entity, simplifying payroll, compliance, and HR administration.
Example: A U.K.-based fintech startup expanding into Southeast Asia can hire Malaysian cybersecurity professionals through FastLaneRecruit’s EOR service. This approach provides immediate access to skilled experts, cost-effective operations, regional compliance knowledge, and flexible scaling without the need to set up a local entity.
Conclusion
The choice between outsourced and in-house cybersecurity ultimately depends on your company’s size, industry, and long-term strategy. While in-house teams provide control and organizational knowledge, outsourcing delivers flexibility, affordability, and access to global expertise.
For many international businesses, the most practical approach is to outsource cybersecurity talent through trusted partners. FastLaneRecruit helps global employers hire skilled cybersecurity professionals in Malaysia via our Employer of Record (EOR) service, giving you instant access to specialized talent without the complexity of setting up a local entity.
Secure Your Business with Top Malaysian Cybersecurity Talent
Don’t wait for a cyberattack to expose vulnerabilities. With FastLaneRecruit, you can quickly and compliantly outsource skilled Malaysian cybersecurity professionals, giving your business 24/7 protection, expertise, and scalability.
Get started today and build a future-proof cybersecurity strategy that keeps your operations safe and your growth on track.


