A Global Employer’s Guide to Payroll, Tax, and Compliance
Expanding your tech team by hiring app developers in Malaysia offers access to a skilled workforce, cost-effective solutions, and a strategic spot in Southeast Asia’s growing digital economy. However, navigating Malaysia’s employment laws, tax regulations, and statutory contributions can be complex, especially if you’re hiring from abroad. This guide provides a clear roadmap to ensure full compliance, minimize risk, and streamline your hiring process.
Also Read: 10 Best Employer of Record (EOR) Services To Consider in 2025
Content Outline
Key Summary
Malaysia is a Prime Destination for Offshore App Developers
Malaysia offers a skilled, English-speaking tech workforce, competitive salaries, a strategic GMT+8 location, and government incentives like MyDIGITAL.
Malaysia’s Employment Laws & Statutory Requirements
Employers must comply with EPF, SOCSO, EIS contributions, and progressive income tax withholding for all employees.
Common Misconceptions About Hiring Offshore
Foreign employers still have tax obligations, contractor misclassification is a risk, and a legal entity is not required if using an EOR.
How an Employer of Record (EOR) Simplifies Hiring
An EOR ensures local compliance, enables fast onboarding, reduces costs, and mitigates employment risks in Malaysia.
Essential Documents for Hiring in Malaysia
Contractors need signed agreements and tax forms, EOR-hired employees require local contracts and benefits enrollment, and direct hires need full payroll, tax, and benefits registration.
Why Choose FastLaneRecruit as Your EOR
FastLaneRecruit handles compliance, payroll, and statutory contributions, enabling fast, legal, and cost-effective hiring of Malaysian talent.
Key Takeaways
- Malaysia is a Prime Destination for Offshore App Developers
Malaysia offers a skilled, English-speaking tech workforce, competitive salaries, a strategic GMT+8 location, and government incentives like MyDIGITAL. - Malaysia’s Employment Laws & Statutory Requirements
Employers must comply with EPF, SOCSO, EIS contributions, and progressive income tax withholding for all employees. - Common Misconceptions About Hiring Offshore
Foreign employers still have tax obligations, contractor misclassification is a risk, and a legal entity is not required if using an EOR. - How an Employer of Record (EOR) Simplifies Hiring
An EOR ensures local compliance, enables fast onboarding, reduces costs, and mitigates employment risks in Malaysia. - Essential Documents for Hiring in Malaysia
Contractors need signed agreements and tax forms, EOR-hired employees require local contracts and benefits enrollment, and direct hires need full payroll, tax, and benefits registration. - Why Choose FastLaneRecruit as Your EOR
FastLaneRecruit handles compliance, payroll, and statutory contributions, enabling fast, legal, and cost-effective hiring of Malaysian talent.
Why Malaysia Is a Prime Destination for Offshore App Developers
Malaysia has emerged as a leading destination for tech outsourcing, drawing attention from global companies looking to scale their development teams efficiently. Its combination of talent, cost advantages, strategic location, and government support makes it particularly appealing for businesses seeking reliable offshore app developers. Here’s why Malaysia stands out:
1. Highly Skilled Workforce
Malaysia’s education system produces a steady pipeline of tech professionals skilled in software development, mobile applications, and IT services. Universities such as Universiti Malaya and Universiti Teknologi Malaysia offer specialized IT and computer science programs, while a growing number of coding bootcamps and private tech schools provide practical, industry-ready skills. Many Malaysian developers are fluent in English, which reduces communication barriers and accelerates project delivery for international teams.
Example: A European startup outsourcing its mobile app development to Malaysia can leverage local talent proficient in both iOS and Android development, reducing training time and improving product quality.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to Western markets like the U.S., UK, or Germany, hiring in Malaysia is significantly more affordable without sacrificing quality. Average salaries for app developers in Malaysia are competitive, allowing businesses to access top-tier skills at a fraction of the cost. This makes Malaysia ideal for startups and SMEs that need high-quality development work but want to manage operational expenses efficiently.
Example: An Australian tech firm can hire two mid-level Malaysian developers for the cost of one developer in Sydney, effectively doubling productivity while maintaining compliance with local labor laws.
3. Strategic Location
Situated in the heart of Southeast Asia, Malaysia provides a convenient time zone (GMT+8) that aligns well with both Asian and Western markets. Its geographic position also serves as a gateway to the broader ASEAN region, facilitating regional expansion and collaboration. Malaysia’s strong digital infrastructure, including reliable internet connectivity in major cities like Kuala Lumpur and Penang, supports remote collaboration with global teams seamlessly.
Example: A U.S.-based company managing a regional software project can coordinate effectively with Malaysian developers during overlapping work hours, ensuring faster iterations and real-time problem-solving.
4. Government Support and Incentives
The Malaysian government actively promotes digital innovation through initiatives such as the Malaysia Digital Economy Blueprint (MyDIGITAL) and MDEC programs. These measures aim to build a strong digital ecosystem by offering incentives to locally established tech companies, R&D grants, and support for foreign investors setting up entities in Malaysia. While overseas businesses outsourcing work to Malaysia may not directly receive these incentives, they still benefit indirectly through access to a more skilled workforce, stronger infrastructure, and competitive local service providers.
Example: A UK-based software company outsourcing app development to a Malaysian partner benefits from the improved talent pool and resources fostered by government programs, even though the incentives apply to local companies.
Also Read: What Is an Onshore and Offshore Team?
Understanding Malaysia’s Employment Laws for Foreign App Developers
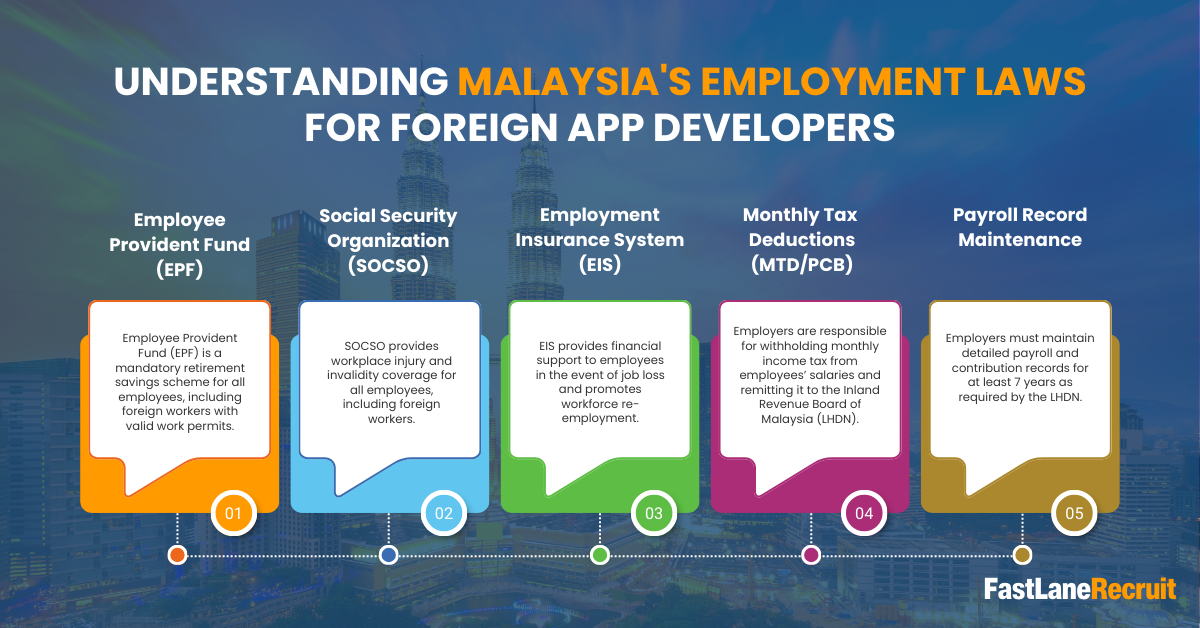
Hiring app developers in Malaysia requires a clear understanding of local employment laws and statutory obligations. Compliance is essential to avoid fines, penalties, or legal complications. Whether you hire through an Employer of Record (EOR) or set up your own entity, you must account for mandatory contributions, tax obligations, and proper record-keeping. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
1. Employee Provident Fund (EPF)
Mandatory Contributions: The Employee Provident Fund (EPF) is a mandatory retirement savings scheme for all employees, including foreign workers with valid work permits. Employers are required to register with EPF and contribute on behalf of their employees. Contributions are made monthly and deposited into the employee’s EPF account, which accumulates over their employment period. (EPF Official Site)
Contribution Rates:
- Employers: 12–13% of the employee’s monthly salary, depending on salary level.
- Employees: 9–11% of monthly salary, based on age and income bracket.
Example: A German startup hires a Malaysian app developer earning MYR 6,000 per month. The employer contributes approximately MYR 720–780 to the EPF, while the employee contributes around MYR 540–660. These contributions are mandatory and legally binding.
2. Social Security Organization (SOCSO)
Coverage: SOCSO provides workplace injury and invalidity coverage for all employees, including foreign workers. It protects both employers and employees against work-related accidents and occupational diseases. Registration is mandatory for every employee from their first day of work. (SOCSO Official Site)
Contribution Rates:
- Employers: 1.25% of the employee’s monthly salary for foreign workers.
- Employees: Not required for foreign employees (contribution is fully employer-funded).
Example: If the same developer earns MYR 6,000, the employer contributes MYR 75 monthly to SOCSO, ensuring the developer is covered under Malaysia’s social security system.
3. Employment Insurance System (EIS)
Mandatory Registration: EIS provides financial support to employees in the event of job loss and promotes workforce re-employment. Employers must register employees with EIS and contribute monthly.
Contribution Rates:
- Employers: 0.2% of monthly salary.
- Employees: 0.2% of monthly salary.
Example: For an employee earning MYR 6,000 per month, both employer and employee contribute MYR 12 each. While this may seem minor, compliance is mandatory and contributes to the employee’s protection and benefits in Malaysia.
Also Read: How To Choose Between In-House or Outsourced Website Development
4. Monthly Tax Deductions (MTD/PCB)
Tax Withholding: Employers are responsible for withholding monthly income tax from employees’ salaries and remitting it to the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (LHDN). This system ensures employees pay their taxes in line with Malaysia’s progressive income tax structure. (LHDN Official Site)
Tax Rates: Malaysia uses progressive tax rates ranging from 0% to 30%, based on total annual income. Employers must calculate and remit accurate deductions each month.
Example: A developer earning MYR 6,000/month may have around MYR 600 withheld for income tax depending on their tax residency status and allowances.
5. Payroll Record Maintenance
Record Keeping: Employers must maintain detailed payroll and contribution records for at least 7 years as required by the LHDN. These records include salary payments, statutory contributions (EPF, SOCSO, EIS), tax deductions, and employee benefits. Proper documentation is critical in case of audits or compliance reviews.
Example: If a company hires five Malaysian developers via an EOR, the EOR handles all record-keeping and reporting, ensuring compliance without burdening the foreign employer.
Key Tip
Navigating Malaysia’s employment laws can be complex for foreign employers. Partnering with a trusted Employer of Record like FastLaneRecruit ensures full compliance with EPF, SOCSO, EIS, tax deductions, and record maintenance, allowing you to focus on hiring top app development talent without legal or administrative risk.
Common Misconceptions About Hiring Offshore Developers
Many global employers hold misconceptions when it comes to hiring app developers in Malaysia. Misunderstanding these points can lead to compliance issues, fines, or mismanaged payroll. Let’s clarify the most common myths and provide tips for avoiding pitfalls.
Also Read: Employer of Record vs. Staffing Agency
1. Hiring Offshore Means No Tax Obligations
Reality: Even if your developers are based overseas, your business may still face tax obligations in both your home country and the developer’s country. Overlooking these requirements can result in double taxation, penalties, or compliance issues.
Example: A U.S. company directly hires a Malaysian developer as an independent contractor. The company must collect a W-8BEN form to confirm the developer’s foreign status and avoid the default 30% U.S. withholding tax. Without it, the company risks overpaying taxes and complicating its accounting.
Tip: Always verify both local and home-country tax requirements before hiring. If you use an EOR like FastLaneRecruit, the EOR becomes the legal employer, manages all local employment compliance in Malaysia, and you won’t need to collect W-8BEN forms from individual employees.
2. Geographical Distance Equals Legal Distance
Reality: Hiring someone overseas does not exempt you from local labor or tax regulations. Even if developers work remotely, obligations can extend to tax reporting, statutory contributions, and employment protections in their country of residence.
Example: A U.S. business paying a Filipino developer directly must still report the payments to the IRS. At the same time, the Philippines may require local tax withholding or employer contributions if the developer is classified as an employee. Non-compliance in either country can result in fines, audits, or reputational damage.
Tip: Map out compliance obligations in both jurisdictions before hiring offshore. With an EOR, your company avoids direct tax and labor liabilities abroad — the EOR manages payroll, taxes, and statutory contributions locally, while you only account for the EOR as a vendor payment in your home country.
Also Read: How to Switch Your EOR Provider
3. No Need for a Legal Entity Overseas
Reality: Setting up a local entity is one way to hire, but it’s often costly, time-consuming, and unnecessary if you’re only building a small team or testing a new market. Without an entity, you would normally be limited to hiring contractors — which creates compliance risks if the role looks more like employment.
Example: A UK-based startup wants to hire three Malaysian developers. Setting up a Malaysian company could take months and require legal registrations, accounting, and ongoing compliance costs. Instead, by partnering with FastLaneRecruit as an EOR, the developers are legally employed under FastLaneRecruit’s Malaysian entity while the UK startup manages day-to-day tasks. Payroll, taxes, and statutory contributions are handled locally by the EOR.
Tip: Use an EOR for rapid market entry. It lets you hire employees in Malaysia immediately without setting up your own entity, while ensuring full compliance with local labor and tax laws.
4. Contractors Are Always Safe to Hire
Reality: Hiring contractors may appear simpler, but there are misclassification risks. If you control their working hours, provide tools, or integrate them into your core operations, authorities may reclassify them as employees. This can trigger back taxes, fines, and obligations for statutory contributions and benefits.
Example: An Australian app company hires a Vietnamese developer as a “contractor” but requires daily stand-up meetings, fixed hours, and provides company hardware. Under local labor law, this arrangement could be deemed employment. Non-compliance may lead to penalties for unpaid social security and employee benefits.
Tip: Use well-defined contracts with clear autonomy and deliverables when engaging contractors. For long-term or structured roles, mitigate misclassification risks by hiring through an EOR. The EOR legally employs the worker, ensuring compliance with local employment laws while you retain control of daily work.
Key Takeaways for Global Employers:
- Understand both home-country and local tax obligations.
- Comply with local labor laws regardless of distance.
- Use an EOR for fast, compliant hiring without setting up a local entity.
- Clearly distinguish contractors from employees to avoid misclassification.
Partnering with a trusted EOR like FastLaneRecruit ensures compliance, mitigates risks, and allows you to focus on managing your offshore developers efficiently.
Also Read: Hiring Malaysian Talent: Employer of Record Malaysia Guide
Simplifying Compliance in Malaysia with an Employer of Record (EOR)
When hiring app developers or other professionals in Malaysia, understanding local employment laws, tax obligations, and statutory contributions can be challenging for foreign employers. An Employer of Record (EOR) provides a practical solution by becoming the legal employer in Malaysia on your behalf, while your hires work directly for your company.
An EOR handles all aspects of local employment, including:
1. Local Employment Contracts
Employment contracts are drafted according to Malaysia’s labor laws, covering working hours, probation periods, termination policies, and statutory benefits. This ensures both the employer and employee remain compliant with the Employment Act 1955.
Example: A UK startup hires two Malaysian developers via an EOR. FastLaneRecruit prepares legally compliant employment contracts in English and Bahasa Malaysia, protecting both parties while meeting statutory requirements.
2. Payroll Processing
The EOR manages payroll in Malaysian Ringgit (MYR), including monthly payslips, deductions, and disbursement of salaries. This eliminates the complexities of converting currencies, understanding local payroll cycles, and managing statutory deductions.
Example: A German company hires three Malaysian developers. FastLaneRecruit ensures salaries are paid on time, EPF and SOCSO contributions are deducted correctly, and monthly payslips are generated automatically.
3. Statutory Contributions
All mandatory contributions, EPF, SOCSO, and EIS, are calculated, deducted, and remitted by the EOR. This ensures compliance with Malaysian statutory requirements without the employer needing to navigate complex regulations.
Tip: Regular updates from the EOR ensure contributions reflect the latest rates and legal changes, preventing penalties or fines.
Also Read: Building Offshore IT Team in Malaysia for Australian Companies
4. Income Tax Withholding and Filing
The EOR handles all local tax compliance, including monthly tax deductions (MTD/PCB) and filing with the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (LHDN). This protects foreign employers from errors and potential audits.
Example: A Canadian company hiring a Malaysian app developer doesn’t need to worry about calculating progressive income tax rates. The EOR calculates, withholds, and remits taxes accurately each month.
5. Employee Benefits Management
The EOR administers statutory benefits such as health insurance, retirement contributions, and unemployment coverage (EIS). This ensures employees receive all legally mandated entitlements while reducing administrative burdens for foreign employers.
Example: When onboarding a new developer, FastLaneRecruit automatically registers them for EPF, SOCSO, and EIS, providing both compliance and peace of mind.
Benefits of Partnering with an EOR in Malaysia
| Benefit | What It Means for Your Business |
| Avoid Entity Setup | Hire top Malaysian talent without registering a local company or office. |
| Ensure Full Compliance | All statutory contributions, tax filings, and labor laws are handled for you. |
| Quick Onboarding | New hires can start working in days, not months, accelerating project timelines. |
| Access Local Expertise | Guidance from HR and payroll teams familiar with Malaysia’s labor laws and workplace practices. |
Example: A Singapore-based tech company wants to hire five app developers in Kuala Lumpur. By partnering with FastLaneRecruit as their EOR, the company can onboard all developers within two weeks, avoid setting up a local entity, and ensure full compliance with Malaysian labor, tax, and social security laws.
Tip: Using an EOR is particularly advantageous for first-time market entry or small teams, as it reduces administrative burden, mitigates legal risks, and allows your business to focus on growth and product development.
Also Read: Building Offshore IT Team in Malaysia for Singapore Companies
Essential Documents When Hiring Internationally in Malaysia
When hiring internationally, having the right documentation is crucial for compliance, smooth payroll operations, and legal protection. Whether you hire contractors, employees through an EOR, or direct hires under your own entity, knowing which documents are required and who handles them can save time, reduce risk, and ensure compliance with Malaysian labor and tax laws.
1. Hiring Contractors
Must-Have Documents:
- Signed Contractor Agreement: Outlines the scope of work, payment terms, project milestones, confidentiality, and intellectual property ownership.
- Tax Residency Forms: For example, U.S. companies require a W-8BEN form from foreign contractors to confirm non-U.S. tax status. Other countries may have local equivalents.
Who Handles It: You or your internal HR/legal team are responsible for preparing the agreement and collecting tax forms.
Example: A Singapore-based marketing agency hires a freelance developer in Malaysia for a 6-month app project. The agency signs a contractor agreement, specifies deliverables, and collects the W-8BEN form to avoid unnecessary withholding tax.
Tip: Clearly define contractor responsibilities, deliverables, and autonomy to reduce misclassification risks under Malaysian law.
2. Hiring Employees via an Employer of Record (EOR)
Must-Have Documents:
- Local Employment Contract: Drafted according to Malaysian labor laws, covering probation periods, working hours, termination clauses, and statutory benefits.
- Tax Registration Forms: The EOR registers the employee with the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (LHDN) for monthly tax deductions (MTD/PCB).
- Benefits Enrollment Documents: Includes mandatory contributions to EPF, SOCSO, and EIS.
Who Handles It: The EOR manages all documentation on your behalf, ensuring full compliance with local employment and tax laws.
Example: A UK-based software company hires two Malaysian developers through FastLaneRecruit. FastLaneRecruit drafts the employment contracts, registers them for EPF, SOCSO, and EIS, and manages monthly payroll and tax filings. The company avoids legal pitfalls and can focus on day-to-day project management.
Tip: Using an EOR ensures that all documents comply with local regulations, reducing the risk of fines or audits.
3. Direct Hire (Own Local Entity)
Must-Have Documents:
- Payroll Setup Documentation: Register employees with Malaysian authorities for EPF, SOCSO, and EIS contributions.
- Tax Filing Registrations: Ensure monthly tax deductions are calculated and remitted correctly.
- Employee Benefits Contribution Forms: Includes retirement savings, social security, and health benefits enrollment.
Who Handles It: Your in-house HR and payroll team or local specialists manage the process.
Example: A German company establishes a subsidiary in Kuala Lumpur. The HR team registers employees for statutory contributions, prepares payroll, and submits monthly tax filings, ensuring full compliance with Malaysian laws.
Tip: Maintaining accurate records of all payroll, tax, and benefits contributions is essential. Malaysia requires employers to keep these records for at least 7 years.
Also Read: Building Offshore IT Team in Malaysia for Hong Kong Companies
Summary Table
| Hiring Type | Must-Have Documents | Who Handles It | Example / Tip |
| Contractor | Signed contractor agreement, tax residency forms | You | Clearly define deliverables to avoid misclassification. Collect W-8BEN or local equivalent for tax compliance. |
| Employee via EOR | Local employment contract, tax registration forms, and benefits enrollment documents | EOR | FastLaneRecruit drafts contracts, registers EPF/SOCSO/EIS, and manages payroll and taxes. |
| Direct Hire (Own Entity) | Payroll setup docs, tax filing registrations, and employee benefits contribution forms | Your in-house HR/payroll team | Keep records for 7 years; ensure compliance with Malaysian labor and tax laws. |
Key Takeaway: Proper documentation is essential when hiring in Malaysia. Partnering with an EOR like FastLaneRecruit ensures all contracts, payroll registrations, tax filings, and statutory contributions are handled accurately, allowing you to hire top talent efficiently while remaining fully compliant.
Conclusion: Hire and Pay Malaysian Developers with Confidence
Hiring app developers in Malaysia offers numerous benefits, but it’s essential to navigate the local employment laws and tax regulations to ensure compliance. Partnering with an Employer of Record (EOR) like FastLaneRecruit simplifies the process, allowing you to focus on building your team and growing your business.
Ready to Hire Offshore Developers in Malaysia?
FastLaneRecruit’s Employer of Record (EOR) service makes it simple for you to hire top Malaysian developers and professionals without setting up a local entity. We take care of everything from employment contracts and payroll processing to statutory contributions, tax compliance, and benefits administration.
With our expert support, you can:
- Hire Fast: Onboard skilled Malaysian talent in days, not months.
- Stay Compliant: We handle all local employment laws and reporting.
- Save Time & Costs: Skip the expense of setting up a company in Malaysia.
- Focus on Growth: While we manage HR, payroll, and compliance in the background.
Ready to scale your global team with peace of mind?
Partner with FastLaneRecruit today and start hiring Malaysian employees compliantly, efficiently, and without the headaches.


